DISCLAIMER : Please note that blog owner takes no responsibility of any kind for any type of data loss or damage by trying any of the command/method mentioned in this blog. You may use the commands/method/scripts on your own responsibility.If you find something useful, a comment would be appreciated to let other viewers also know that the solution/method work(ed) for you.
6 Strategies for Migrating Applications to the Cloud
Formulating a Migration Strategy
Enterprises typically begin to contemplate how to migrate an application during the second phase of the “Migration Process” — Portfolio Discovery and Planning. This is when they determine what’s in their environment, what are the interdependencies, what’s going to be easy to migrate and what’s going to be hard to migrate, and how they’ll migrate each application.
Using this knowledge, organizations can outline a plan (which should be considered subject to change as they progress through their migration and learn) on how they’ll approach migrating each of the applications in their portfolio and in what order.
The complexity of migrating existing applications varies, depending on the architecture and existing licensing arrangements. If I think about the universe of applications to migrate on a spectrum of complexity, I’d put a virtualized, service-oriented architecture on the low-complexity end of the spectrum, and a monolithic mainframe at the high-complexity end of the spectrum.
I suggest starting with something on the low-complexity end of the spectrum for the obvious reason that it will be easier to complete — which will give you some immediate positive reinforcement or “quick wins” as you learn.
6 Application Migration Strategies: “The 6 R’s”
The 6 most common application migration strategies we see are: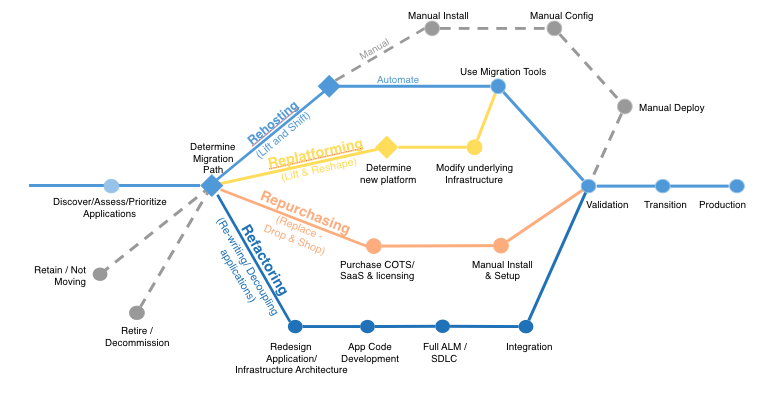
1. Rehosting — Otherwise known as “lift-and-shift.”
We find that many early cloud projects gravitate toward net new development using cloud-native capabilities, but in a large legacy migration scenario where the organization is looking to scale its migration quickly to meet a business case, we find that the majority of applications are rehosted. GE Oil & Gas, for instance, found that, even without implementing any cloud optimizations, it could save roughly 30 percent of its costs by rehosting.
Most rehosting can be automated with tools (e.g. AWS VM Import/Export, Racemi), although some customers prefer to do this manually as they learn how to apply their legacy systems to the new cloud platform.
We’ve also found that applications are easier to optimize/re-architect once they’re already running in the cloud. Partly because your organization will have developed better skills to do so, and partly because the hard part — migrating the application, data, and traffic — has already been done.
2. Replatforming — I sometimes call this “lift-tinker-and-shift.”
Here you might make a few cloud (or other) optimizations in order to achieve some tangible benefit, but you aren’t otherwise changing the core architecture of the application. You may be looking to reduce the amount of time you spend managing database instances by migrating to a database-as-a-service platform like Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS), or migrating your application to a fully managed platform like Amazon Elastic Beanstalk.
A large media company we work with migrated hundreds of web servers it ran on-premises to AWS, and, in the process, it moved from WebLogic (a Java application container that requires an expensive license) to Apache Tomcat, an open-source equivalent. This media company saved millions in licensing costs on top of the savings and agility it gained by migrating to AWS.
3. Repurchasing — Moving to a different product.
I most commonly see repurchasing as a move to a SaaS platform. Moving a CRM to Salesforce.com, an HR system to Workday, a CMS to Drupal, and so on.4. Refactoring / Re-architecting — Re-imagining how the application is architected and developed, typically using cloud-native features.
This is typically driven by a strong business need to add features, scale, or performance that would otherwise be difficult to achieve in the application’s existing environment.Are you looking to migrate from a monolithic architecture to a service-oriented (or server-less) architecture to boost agility or improve business continuity (I’ve heard stories of mainframe fan belts being ordered on e-bay)? This pattern tends to be the most expensive, but, if you have a good product-market fit, it can also be the most beneficial.
5. Retire — Get rid of.
Once you’ve discovered everything in your environment, you might ask each functional area who owns each application. We’ve found that as much as 10% (I’ve seen 20%) of an enterprise IT portfolio is no longer useful, and can simply be turned off. These savings can boost the business case, direct your team’s scarce attention to the things that people use, and lessen the surface area you have to secure.6. Retain — Usually this means “revisit” or do nothing (for now).
Maybe you’re still riding out some depreciation, aren’t ready to prioritize an application that was recently upgraded, or are otherwise not inclined to migrate some applications. You should only migrate what makes sense for the business; and, as the gravity of your portfolio changes from on-premises to the cloud, you’ll probably have fewer reasons to retain.Linux booting issues and solutions
Here I am going to see how to resolve few of the common booting issues in Linux.
Option 1: init not found error
Option 2: Run fsck on all FS in rescue mode
Option 3: Reinstall GRUB
Option 4: Recover grub.conf / grub configuration
Error : "init not found" displayed
1) Launch the system to Bash shell prompt
Reboot the server and interrupt to edit the GRUB.
Edit grub and enter the below in last
init=/bin/bash
Then save and exit and boot the server. This will launch you straight into a Bash shell prompt.Then you can remount “/” file system and check /var/log/messages for any error.
Note : init=/bin/bash (Grub boot loader) or linux init=/bin/bash (if Lilo boot loader).
2) Once server booted and if it is in Bash shell prompt
#mount -o remount,rw /
3) Now you can check the log messages and try to find the reason for server pacnic or error.
#more /var/log/messages
1) Boot from the Linux First CD (boot CD).
2) Type “boot rescue” at Linux boot prompt.
3) After the bash shell prompt show up, type the below command
# chroot /mnt/sysimage
a) Run fsck and Check for any disk error
#fdisk -l /dev/sda //check how many partion you have
then run fsck on each partition
#fsck -y /dev/sda2'
In rescue mode.
# chroot /mnt/sysimage
# /sbin/grub-install /dev/hda
(possibly caused by incorrect changes to the the GRUB configuration file, installation of another OS, changes to device ordering due to hardware or BIOS changes, etc.)
# grub> find /boot/grub/grub.conf (or) grub>find /grub/grub.conf (or) find /boot/grub/stage1
(hd0,1)
(hd1,2)
>> This tells us that we have two /boot partitions. Then we have to reinstall the GRUB config on disk (one by one) and try.
#grub> root (hd0,1) //Write the GRUB boot loader on the MBR of the first disk
grub> setup (hd0)
grub>quit
If you have doubt as to where the root partition is located then try to find a file in /etc.
#grub> find /etc/fstab
(hd0,1)
Note: You must pay attention to your devices, for me "hd0" is the root disk and (hd0,1) is /boot partition , and (hd0,1) is my ROOT (/) partition. mostly / "root" partion will be on LVM.
You might not even have "hd0" mapped out. Review your "/boot/grub/device.map" file
#cat /boot/grub/device.map
Option 1: init not found error
Option 2: Run fsck on all FS in rescue mode
Option 3: Reinstall GRUB
Option 4: Recover grub.conf / grub configuration
Option 1: For normal panic and "init not found" error.
Error : "init not found" displayed
1) Launch the system to Bash shell prompt
Reboot the server and interrupt to edit the GRUB.
Edit grub and enter the below in last
init=/bin/bash
Then save and exit and boot the server. This will launch you straight into a Bash shell prompt.Then you can remount “/” file system and check /var/log/messages for any error.
Note : init=/bin/bash (Grub boot loader) or linux init=/bin/bash (if Lilo boot loader).
2) Once server booted and if it is in Bash shell prompt
#mount -o remount,rw /
3) Now you can check the log messages and try to find the reason for server pacnic or error.
#more /var/log/messages
Option 2: If the above option not helped then follow the next
1) Boot from the Linux First CD (boot CD).
2) Type “boot rescue” at Linux boot prompt.
3) After the bash shell prompt show up, type the below command
# chroot /mnt/sysimage
a) Run fsck and Check for any disk error
#fdisk -l /dev/sda //check how many partion you have
then run fsck on each partition
#fsck -y /dev/sda2'
Option 3: If the above also not helped then try to reinstall grub and retry.
In rescue mode.
# chroot /mnt/sysimage
# /sbin/grub-install /dev/hda
Option 4: If a system has issues with the GRUB configuration
(possibly caused by incorrect changes to the the GRUB configuration file, installation of another OS, changes to device ordering due to hardware or BIOS changes, etc.)
# grub> find /boot/grub/grub.conf (or) grub>find /grub/grub.conf (or) find /boot/grub/stage1
(hd0,1)
(hd1,2)
>> This tells us that we have two /boot partitions. Then we have to reinstall the GRUB config on disk (one by one) and try.
#grub> root (hd0,1) //Write the GRUB boot loader on the MBR of the first disk
grub> setup (hd0)
grub>quit
If you have doubt as to where the root partition is located then try to find a file in /etc.
#grub> find /etc/fstab
(hd0,1)
Note: You must pay attention to your devices, for me "hd0" is the root disk and (hd0,1) is /boot partition , and (hd0,1) is my ROOT (/) partition. mostly / "root" partion will be on LVM.
You might not even have "hd0" mapped out. Review your "/boot/grub/device.map" file
#cat /boot/grub/device.map
Difference between RHEL6 and RHEL7
Below are the major differences between RHEL 6 and 7.
On the release date for 6 & 7
RHEL 6: 10 NOV 2010
RHEL 7: 10 JUNE 2014
The latest is RHEL 7
Difference on the basis of operating system names
if we want to see use this command
# cat /etc/redhat-release
RHEL 6: SANTIGO
RHEL 7: MAIPO
Kernel version
If we want to see in terminal use this command: lsb_release -a or uname -a
RHEL 6: 2.6.32
RHEL 7: 3.0.10
OS boot time
RHEL 6: 40 sec
RHEL 7: 20 sec
Maximum size of single partition
RHEL 6: 50TB(EXT4)
RHEL 7: 500TB(XFS)
Boot loader
RHEL 6: /boot/grub/grub.conf
RHEL 7: /boot/grupb2/grub.cfg
Processor architecture
RHEL 6: It support 32bit & 64bit both
RHEL 7: It only support 64bit
How to format or assign a file system in
RHEL 6: # mkfs.ext4 /dev/hda6
RHEL 7: # mkfs.xfs /dev/hda6
How to repair a file system in
RHEL 6: # fsck -y /dev/hda6
RHEL 7: # xfs_repair /dev/hda6
Command to manage network
RHEL 6: # setup
RHEL 7: # nmtui
Host name configuration file
RHEL 6: /etc/sysconfig/network
RHEL 7: /etc/hostname
Default ISO image mount path
RHEL 6: /media
RHEL 7: /run/media/root
File system check
RHEL 6: e2fsck
RHEL 7: xfs_repair
Resize a filesystem
RHEL 6: # resize2fs -p /dev/vg00/lv1
RHEL 7: # xfs_growfs /dev/vg00/lv1
Tune a filesystem
RHEL 6: tune2fs
RHEL 7: xfs_admin
IP tables and firewalls
RHEL 6: iptables
RHEL 7: firewalled
Communication between TCP and UDP in backend
RHEL 6: netcat
RHEL 7: ncat
Interface name
RHEL 6: eth0
RHEL 7: ens198(N)
Combining NIC
RHEL 6: Network Bonding
RHEL 7: Team Driver
NFS server version
RHEL 6: NFSv2
RHEL 7: NFSV4
Database used
RHEL 6: Mysql
RHEL 7: mariaDB
Managing services
RHEL 6:
# service sshd restart
# chkconfig sshd on
RHEL 7:
# systemctl restart sshd
# systemctl enable shhd



